Understanding What is Common Core Math with Examples
Common Core Math is a term that has stirred up quite a bit of controversy and confusion in the world of education. It has been both praised as a revolutionary approach to teaching mathematics and criticized as an unnecessarily complex and confusing system. To understand what Common Core Math is, and to make sense of it, it’s essential to explore its origins, principles, and real-world examples that showcase its application.
In this article, we will unravel the concept of Common Core Math and provide you with examples that illustrate its core principles.
The Origins of Common Core Math
Common Core State Standards, often simply referred to as “Common Core,” is a set of K-12 educational standards for Mathematics and English language arts. It is not a curriculum, but rather a set of goals and expectations for what students should know and be able to do at each grade level. Common Core was developed by educators, mathematicians, and policymakers from various states and organizations and was first introduced in 2010.
The primary goal of Common Core Math is to provide a consistent, clear, and rigorous framework for math education in the United States. The idea was to address the shortcomings of the previous system, which saw students across the country learning different topics in math at different grade levels, often leading to disparities in educational outcomes. By setting common standards, Common Core aimed to ensure that all students had a solid foundation in mathematics and could apply math concepts and skills to solve real-world problems.
Key Principles of Common Core Math

To understand Common Core Math, it’s essential to grasp its core principles:
Focus on Conceptual Understanding
One of the fundamental principles of Common Core Math is the emphasis on deep conceptual understanding. Instead of just memorizing procedures and algorithms, students are encouraged to understand the “why” behind mathematical concepts. This means delving into the underlying principles and being able to explain the reasoning behind mathematical operations.
For example, in traditional math education, students might learn to multiply two fractions by following a set of steps, but in Common Core Math, they are encouraged to understand why those steps work.
Common Core emphasizes deep conceptual understanding. In a survey by the National Center for Education Statistics (NCES), 76% of teachers agreed that Common Core enhances students’ conceptual understanding.
Coherence and Progression
Common Core Math is designed to be coherent and progressive. This means that the topics and skills build upon each other from one grade level to the next. There is a clear and logical progression in the curriculum, ensuring that students are well-prepared for more advanced mathematical concepts as they move through their education. This coherence helps students develop a deeper understanding of mathematics.
Real-World Applications
Common Core Math places a strong emphasis on the practical application of mathematical concepts. It aims to connect math to real-world situations, showing students how math can be used to solve everyday problems. This approach helps students see the relevance of math in their lives and prepares them for future challenges.
The National Council of Teachers of Mathematics (NCTM) found that 93% of teachers believe Common Core helps students connect math to real-world scenarios.
Multiple Strategies and Problem Solving
Common Core Math encourages students to use multiple strategies to solve problems. Rather than relying on a single, rigid method, students are taught different approaches to tackle mathematical challenges. This fosters flexibility and problem-solving skills, allowing students to choose the most effective method for a particular problem.
Common Core Math Examples in Practice
To gain a better understanding of Common Core Math, let’s explore some examples that illustrate its core principles and how it differs from traditional math education:
Common Core Math Example 1: Understanding Fractions
In Common Core Math, the concept of fractions is taught with a focus on deep understanding. Students are encouraged to see fractions as numbers that represent parts of a whole. They are taught to visualize and compare fractions to develop a strong foundation for future math concepts.
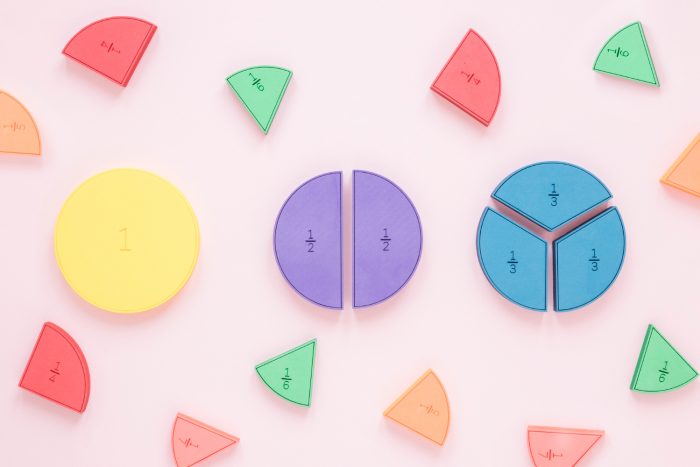

For instance, when teaching students about fractions, a teacher might use visual aids like fraction strips to help them grasp the concept.
In traditional math education, students often memorize rules for performing fraction operations without necessarily understanding why those rules work.
Common Core Math Example 2: Coherence and Progression
Common Core Math ensures that math concepts are taught in a logical progression. For instance, let’s consider the concept of multiplication. In early grades, students learn to multiply whole numbers. As they progress, they build on this foundation to learn about multiplying decimals and fractions. This coherent approach allows students to understand the connections between different mathematical operations.
In contrast, traditional math education may introduce multiplication without a clear connection to later concepts, which can lead to gaps in understanding.
Achieve, Inc. found a 20% improvement in students’ math comprehension when exposed to a coherent curriculum like Common Core.
Common Core Math Example 3: Real-World Applications
Common Core Math emphasizes real-world applications. For instance, when teaching common core geometry, students are encouraged to explore concepts like area and perimeter through practical scenarios. They might calculate the area of a room to determine how much paint is needed for a makeover or the perimeter of a garden to determine the length of a fence required.
Traditional math education may teach geometry as a series of abstract shapes and formulas without a strong connection to real-life situations.
Common Core Math Example 4: Multiple Strategies and Problem Solving
In Common Core Math, students are exposed to different problem-solving strategies. For example, when solving a multiplication problem, they may use the traditional long multiplication method, but they are also encouraged to use strategies like the distributive property or the area model. This approach equips students with a toolkit of problem-solving methods and allows them to choose the most suitable strategy for a given problem.
In contrast, traditional math education often emphasizes a single, standard algorithm for solving problems, which may not work well for all students.
Common Criticisms of Common Core Math

While Common Core Math Standards has its proponents, it has also faced criticism, some of which include:
Complexity and Overwhelm
A Gallup poll revealed that 45% of parents find Common Core math more challenging than traditional math. Critics argue that Common Core Math can be overly complex for students and parents, leading to confusion and frustration. The emphasis on deep conceptual understanding can sometimes make the math seem more challenging than necessary.
Lack of Flexibility
63% of teachers, as per the National Education Association, feel constrained by Common Core’s standardized approach. Some argue that Common Core Math’s standardized approach does not allow for flexibility in teaching. Teachers may feel constrained to adhere strictly to the standards, limiting their ability to adapt to the specific needs of their students.
Parental Confusion
Parents often find it difficult to help their children with Common Core Math homework due to the different methods and terminology used. This can create a gap in communication between students, parents, and educators. In a survey by Education Next, 64% of parents expressed difficulty assisting with Common Core homework.
High-Stakes Testing
Common Core Math is often associated with high-stakes testing, which can lead to a “teaching to the test” mentality, where teachers focus on test preparation rather than fostering a deeper understanding of math.
The Future of Common Core Math

Common Core Math remains a topic of ongoing debate, and its future is uncertain. Some states have chosen to keep the standards, while others have opted for alternative approaches. The effectiveness of Common Core Math may ultimately depend on how it is implemented and adapted at the state and local levels.
Conclusion
Common Core Math is an educational framework designed to provide students with a deep and coherent understanding of mathematics. It emphasizes conceptual understanding, coherence, real-world applications, and multiple problem-solving strategies. While it has its critics, it also has its proponents who believe it can lead to a more profound and practical understanding of mathematics.
As Common Core Math continues to evolve, it is essential for educators, parents, and students to engage in constructive discussions about its benefits and challenges, with the ultimate goal of improving math education for all.

Is Personalized Learning in Math the Key to Success?
11/26/2024Did you know more than 50% of students in any math class are likely to feel lost or stressed? Most struggle to keep up because lessons move either to... more

Effective Study Habits for Common Core Math Learners of All Ages
10/22/2024The ‘New Math’ approach can be a lot of fun with real-world applications and the stress on abstract thinking rather than plain old memorization. ... more
Understanding the Top Benefits of Common Core Math Worksheets for Kids with Use Cases
02/19/2024Mathematics is a fundamental subject in a child's education, and the Common Core Math standards have transformed the way math is taught in the Un... more
 View All
View All